REST vs GraphQL: Which Should You Use?
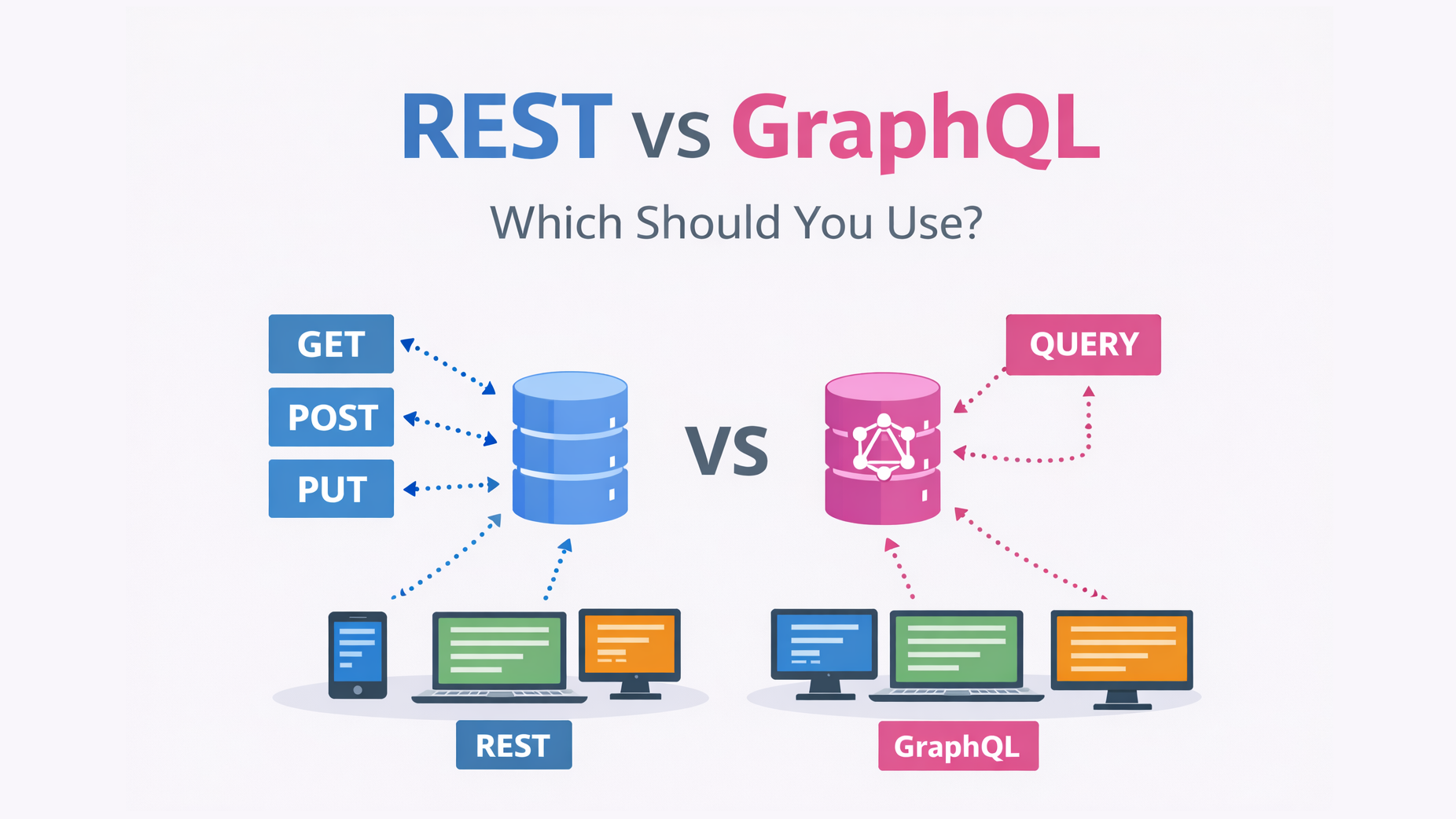
When building APIs, one of the most common questions is:
Should I use REST or GraphQL?
Both are widely used, powerful, and solve similar problems — but in very different ways.
This article compares REST and GraphQL from a practical developer perspective so you can choose the right one for your project.
🔹 What is REST?
REST (Representational State Transfer) is an architectural style based on HTTP and resources.
You access data using endpoints like:
GET /users
GET /users/123
POST /users
Each endpoint represents a resource.
Key characteristics:
- Multiple endpoints
- Uses HTTP verbs (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE)
- Responses are fixed per endpoint
🔹 What is GraphQL?
GraphQL is a query language and runtime for APIs.
Instead of multiple endpoints, GraphQL uses a single endpoint and allows clients to request exactly what they need.
Example:
query {
user(id: 123) {
id
name
posts {
title
}
}
}
🔹 Core Differences
| Feature | REST | GraphQL |
|---|---|---|
| Endpoints | Many | Single |
| Data fetching | Fixed | Client-defined |
| Over/under-fetching | Common | Solved |
| Versioning | Needed | Rare |
| Caching | HTTP native | Manual |
| Learning curve | Low | Medium |
🔹 Over-fetching vs Under-fetching
REST Example:
To get user + posts:
GET /users/123
GET /users/123/postsYou might get more or less data than needed.
GraphQL:
You request exactly what you need in one call.
🔹 When to Use REST
Use REST if:
- You want simplicity
- Your data model is simple
- You want easy caching
- You are building public APIs
🔹 When to Use GraphQL
Use GraphQL if:
- Clients need flexible data
- You have multiple frontends (web, mobile)
- You want fewer requests
- You need strong typing
🔹 Performance
REST can be faster for simple requests and caching.
GraphQL can reduce network usage but requires more server-side processing.
🔹 Security
GraphQL needs protection against:
- Deep nested queries
- Expensive queries
REST relies on standard HTTP protections.
🔹 Conclusion
| Use REST | Use GraphQL |
|---|---|
| Simple APIs | Complex data |
| Public APIs | Multiple clients |
| Heavy caching | Flexible queries |
| Low learning curve | Strong typing |
Neither is better — they solve different problems.